A Deep Dive into High Voltage Cables for EVs and Energy Storage
2023-12-22|
Table of contents: |
Net Zero Emissions is a global trend, and the electric vehicle and energy storage industries are at the forefront of this green energy wave. High-voltage cables, as a core component in both fields, will be thoroughly explored in this article, focusing on the key advantages of the high-voltage cables we produce.
What is a high-voltage cable?
High-voltage cables, also known as high-tension cables or HV cables, are used to transmit high-voltage electrical power. Typically, the voltage level of high-voltage cables is 1000V or higher, encompassing different levels like medium voltage, high voltage, extra-high voltage, and ultra-high voltage.

Voltage Level Standards (may vary by country or region):
-
Low Voltage
Low voltage usually refers to voltages below 1kV. It is commonly used in homes, businesses, and smaller industrial applications. Common examples include 110V and 220V.
-
Medium Voltage
Voltages between 1kV and 33kV fall into the medium voltage category. Medium voltage is commonly found in industrial settings, large commercial facilities, and some power plants.
-
High Voltage
High voltage is mainly used in power transmission and distribution systems, including cables, substations, and power grids.
Material and structure of high-voltage cables
The structure of high-voltage cables primarily involves conductors and insulation. Additional shielding layers and outer jackets may be added based on the specific application and environmental conditions.
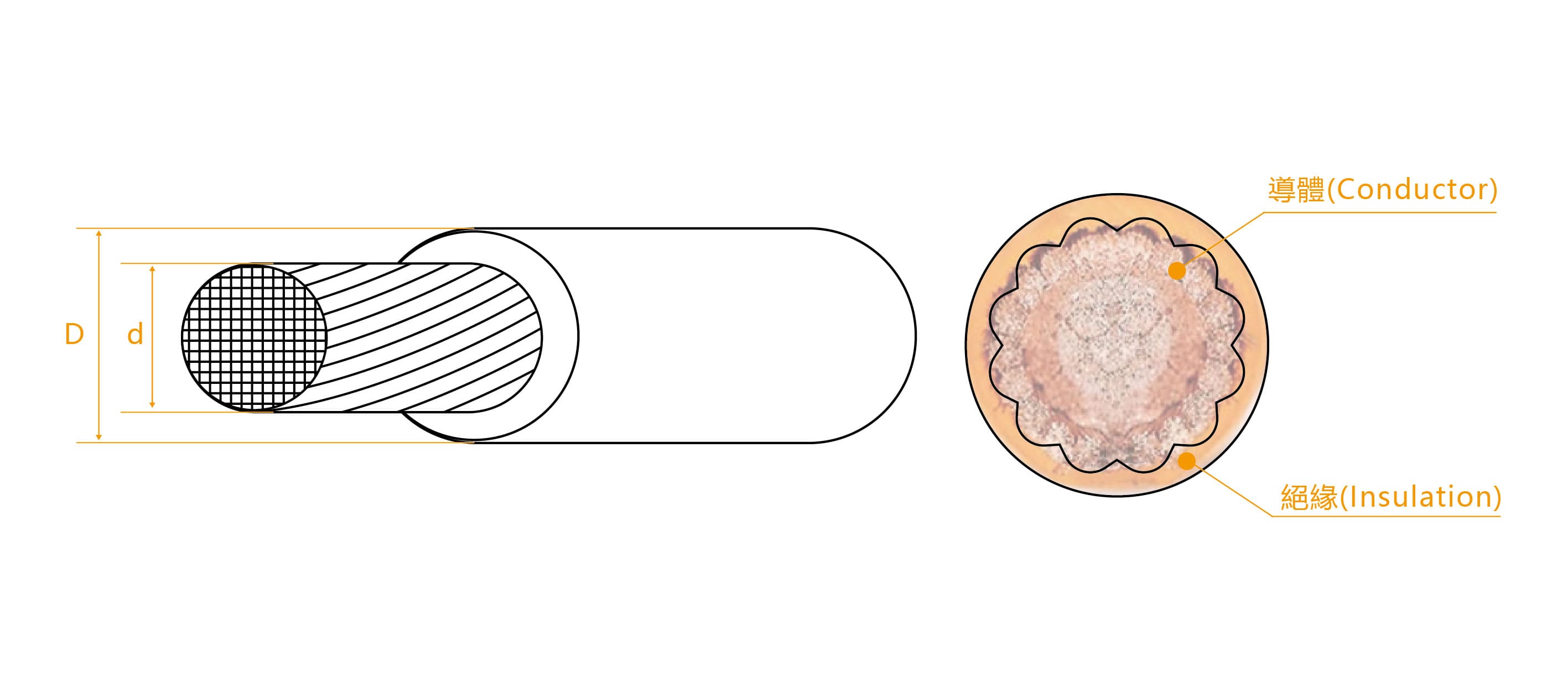
-
Conductor
Common conductor materials include copper (Cu) and aluminum (Al). They have excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for high-voltage environments. Conductors are usually designed in round or flat shapes based on the wire's purpose and current requirements.
-
Insulation
Common insulation materials include polyethylene (PE), cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), rubber, and more. These materials effectively block electrical currents, preventing leakage and short circuits.
Advantages of the XLPE insulation used in Good Gi high-voltage cables:
-
High insulation performance - effectively blocks electrical currents, reducing the risk of leakage and loss.
-
Good heat resistance - remains stable at high temperatures.
-
Improved mechanical strength - exhibits higher tensile strength and wear resistance.
-
Chemical corrosion resistance - suitable for specific environmental applications.
-
-
Shield
The shield is typically made of materials with good conductivity, such as copper wire braiding or copper foil. It is used to reduce the impact of external electromagnetic interference on the cable.
-
Outer Sheath
As the name suggests, the outer sheath is the outermost layer of the cable. It is made of durable materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyethylene (PE), providing resistance to wear, oil, water, and weather.
High voltage cable for Electric vehicle
Primarily used in the power system of electric vehicles, transmitting power to drive electric motors. This includes connections between the battery and electric motor and various control systems within the vehicle. High-voltage cables are crucial in electric vehicles, directly impacting performance, efficiency, and safety.
Requirements for Electric Vehicle High-Voltage Cables:
-
High Voltage and Wear Resistance High-voltage cables in electric vehicles must endure high-voltage environments and resist prolonged wear and tear.
-
Insulation Due to the nature of high voltage, the cable's insulation material must provide excellent insulation to prevent current leakage.
-
High Temperature Resistance In electric vehicle power systems, high-voltage cables often face high-temperature conditions and need to operate stably over extended periods.
-
Lightweight and Flexibility Electric vehicles tend to be heavier than traditional fuel vehicles. Reducing the weight of high-voltage cables helps decrease energy consumption, potentially improving driving range and enhancing maneuverability and acceleration.
-
Flame Retardant Fire incidents in electric vehicles pose a serious safety risk and are challenging to extinguish. Therefore, flame retardancy is a fundamental and essential requirement for electric vehicles.
Good Gi's electric vehicle high-voltage cables.
3820 electric vehicle high-voltage cables - 1000V
3886 electric vehicle high-voltage cables - 1500V
High voltage cable for energy storage cabinet
Primarily used in energy storage systems, especially in energy storage cabinets or systems, to connect batteries, inverters, and power management systems. These wires play a crucial role inside energy storage cabinets, assisting in the storage, conversion, and distribution of energy.
Requirements for Energy Storage Cabinet High-Voltage Cables:
-
High Voltage and Efficiency High-voltage cables used in energy storage cabinets must withstand high voltage while ensuring efficient power transmission to maintain the system's performance.
-
Durability Given the frequent charge and discharge cycles in energy storage cabinet operations, corresponding high-voltage cables need to exhibit good durability to withstand prolonged use.
-
Insulation Similar to high-voltage cables in electric vehicles, those in energy storage cabinets require excellent insulation performance to prevent current leakage and loss.
-
Adaptability to Different Environments Energy storage cabinets may operate under various environmental conditions. Therefore, high-voltage cables need to adapt to different temperatures, humidity levels, and chemical environments.
-
Fire Retardancy for Safety Energy storage cabinets contain high-energy-density battery systems, and in case of accidents, there is a risk of fire. Hence, the cables need to possess fire-resistant and flame-retardant properties to enhance system safety and reduce the risk of fire spread.
Good Gi's energy storage high-voltage cables.
3820 energy storage high-voltage cables - 1000V
3886 energy storage high-voltage cables - 1500V
High voltage cable UL certification
Good Gi manufactures high-voltage cables that meet the UL 3820 and UL 3886 certification standards. The UL certification number for Good Gi is E538616. Led by Underwriters Laboratories (UL), these standards have strict safety and performance requirements to ensure the stability and reliability of the cables during use. The testing standards for UL 3820 and UL 3886 are provided below:
UL 3886 certification
-
Rating: 125 deg C, 1500 Vac, Horizontal flame.
-
Conductor: 44 AWG - 2000 kcmil, solid or stranded.
-
Insulation: XLPE, 30 mils minimum average thickness, 27 mils minimum thickness at any point.
-
Standard: Appliance Wiring Material UL 758.
UL 3820 certification
-
Rating: 125 deg C, 1000 Vac Horizontal flame.
-
Conductor: 30 - 2000 kcmil, solid, stranded, or braided, tinned, bare or silver-plated copper or solid or stranded coated high strength copper - minimum 90 percent conductivity.
-
Insulation: Extruded XLPE.
Conductor size
Min average thickness (mils)
Min at any point thickness (mils)
30-9 AWG
30
27
8-2 AWG
45
40
1-4/0 AWG
55
50
213-500 kcmil
65
58
501-1000 kcmil
80
72
1001-2000 kcmil
95
86
-
Standard: Appliance Wiring Material UL 758.
How do you choose between UL 3886 and UL 3820?
When selecting high-voltage cables like UL 3886 or UL 3820, a comprehensive assessment based on specific application requirements is necessary. Here are key points to consider:
Differences between UL 3886 and UL 3820:
Through a comparison of the above UL certification standards, we can identify the main distinctions between UL 3886 and UL 3820 in terms of rated voltage and insulation thickness.
Applications and Uses:
UL 3886: It has a higher-rated voltage and a thinner insulation layer. This makes it suitable for internal wiring in electric vehicles, allowing flexibility in tight spaces. Compared to the thicker insulation of UL 3820, the thinner insulation of UL 3886 contributes to a lighter overall weight.
UL 3820: It has a thicker insulation layer, offering excellent wear resistance. As there are no specific tests for wear resistance in UL standards, when assessing application environments, users are advised to consider installation conditions and construction situations.
Choosing between UL 3886 and UL 3820 high-voltage cables requires understanding their differences and evaluating them based on specific application needs. Our team, with extensive industry experience, can provide the most suitable solutions for your requirements. Contact us now!